Know the symptoms of heart disease like chest discomfort, difficulty of breathing and tiredness. Read about the early signs of heart diseases, potential diagnosis procedures and ways of how to prevent this serious problems.
Cardiovascular disease or more commonly known as heart disease is the number one killer disease worldwide and causes millions of deaths yearly. However, most individuals still lack formal knowledge of symptoms of heart disease or simply overlook them when they appear. We need to recognize signs of the disease in its early stage before it develops complications and cause more deaths. This article will give you more information about heart disease testing, its signs, different forms, and how to avoid it. The focus is on educating the reader and therefore giving him sufficient information with which he will have to take charge of his heart.
Understanding Heart Disease
What Is Heart Disease?
Heart disease includes numerous diseases of the circulatory system, in particular of the heart. These conditions can alter the normal rhythm and function of the heart so you should keep a check on them.
Common types of heart disease include:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): It is a disease characterized by narrowing of the blood vessels supplying the heart muscles usually due to blood clots.
- Arrhythmias: Irregular heart rhythms that can affect the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively.
- Heart Failure: A disease that the heart cannot pump blood to the body organs as required by the body.
- Heart Valve Disease: A condition of one or more heart valves not working correctly – that is not opening and shutting effectively to allow the correct volume of blood to flow throughout the body.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Congenital conditions that exists at birth that affects the patient’s anatomy.
The Prevalence of Heart Disease
The latest estimates of the WHO reveal that every year 17.9 million people die from cardiovascular diseases, although total of 56 million, which is 31% of all deaths in the world. Even though different medical techniques are used to treat heart diseases, there still remains a rise in prevalence due to individual habits, and aging populations.
Causes and Risk Factors
Heart disease is caused by a combination of modifiable and non-modifiable factors:
- Modifiable Risk Factors:
- Poor diet high in saturated fats and processed foods.
- Lack of physical activity.
- Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Obesity and being overweight.
- High blood pressure (hypertension).
- High cholesterol levels.
- Non-Modifiable Risk Factors:
- Age (higher risk in older adults).
- Family history of heart disease.
- Ethnicity (some ethnic groups are at higher risk).
- Gender (men are generally at higher risk, although women’s risk increases after menopause).
Symptoms of Heart Disease
Common Symptoms
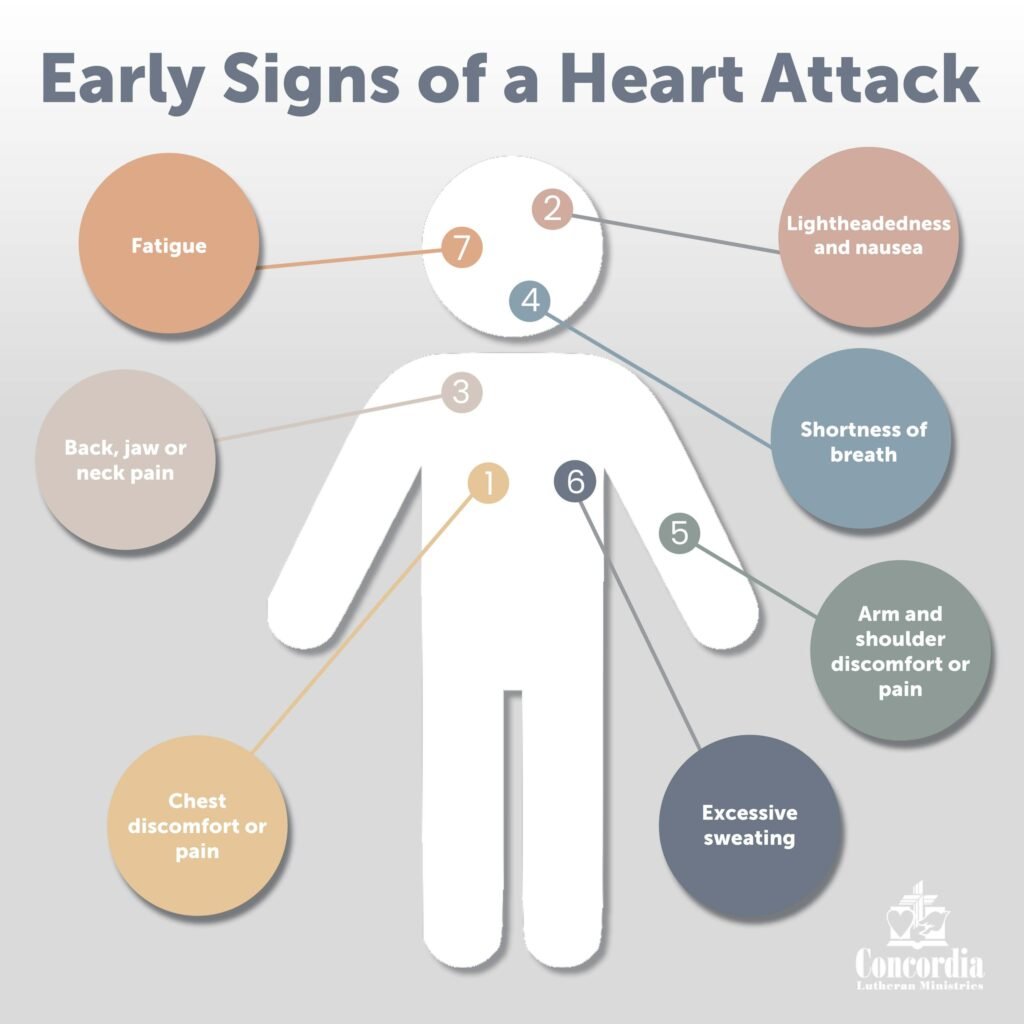
Symptoms of heart disease can vary depending on the specific condition but often include:
- Chest Pain or Discomfort:
- Commonly claimed as a pressure, constriction, or a sensation equivalent to holding the breath in the chest.
- Commonly associated with coronary artery disease or a heart attack.
- Shortness of Breath:
- Shortness of breath with activities, such as exercise, or while at rest.
- It can be a sign of heart failure or problem with the valves.
- Fatigue:
- Fatigue and weakness, especially when the candidate was barely active suggest a probable heart problem.
- Swelling (Edema):
- Edema that can occurs in legs, ankles, feet, or abdomen because of fluids accumulation.
- Sometimes, a sign of heart failure.
- Palpitations:
- Palpitations, a feeling that is described as victim experiencing his or her heartbeat as irregular, fast or pounding.
- Pain in Other Areas:
- Some chest pain may be referred to the arms, neck, jaw, shoulder, or back due to detection by the sympathetic nervous system.
- Nausea, Dizziness, or Lightheadedness:
- May develop during an acute myocardial infarction or because of the presence of arrhythmias.
Gender Differences in Symptoms
Heart disease manifests differently in men and women:
- Men: Frequently the patient is much more likely to experience these more classic symptoms such as chest pain and shortness of breath.
- Women: They may developed milder symptoms, like nausea, fatigue, and upper back or jaw pain, which is not as apparent as the usual symptoms of a heart attack.
Silent Symptoms
Some may, however, have non-specific or even ‘silent’ symptoms particularly in conditions like silent heart attacks. These symptoms are vague and common and likely to be confused with other diseases such as ulcers or muscle sprain.
Diagnosing Heart Disease
It is therefore important to have early diagnosis in order to enable treatment and management. Diagnostic processes for heart disease include:
- Medical History and Physical Examination:
- Primary appraisal involves evaluation of complaints common to the patient, his or her lifestyle and history of other family members.
- Primary appraisal involves evaluation of complaints common to the patient, his or her lifestyle and history of other family members.
- Diagnostic Tests:
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): This records electrical signals of the heart in order to diagnose abnormalities.
- Echocardiogram: Traditionally called echocardiography – It utilizes sound waves to map structures of the heart and how it works.
- Stress Test: Assesses the efficiency of the heart during exercise.
- Blood Tests: Checks count of cholesterol, troponin and glucose.
- Angiography: Provides an X-ray to determine if the coronary arteries are blocked.
- Advanced Imaging Techniques:
- CT or MRI Scans: Give clear pictures of the heart and blood vessels.
- Nuclear Heart Scan: Determines blood supply adequacy and categorizes affected heart tissue.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Recognizing when symptoms require immediate medical attention can save lives. Seek emergency care if you experience:
- Persistent chest pain lasting more than a few minutes.
- Severe shortness of breath.
- Sudden fainting or dizziness.
- Pain radiating to the arms, back, or jaw.
- Rapid or irregular heartbeat accompanied by other symptoms.
Preventing Heart Disease
While some risk factors cannot be controlled, adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of heart disease. Here are key preventive measures:
1. Maintain a Heart-Healthy Diet
- Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
- Limit intake of saturated fats, trans fats, sugar, and salt.
2. Stay Physically Active
- Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise weekly.
- Incorporate strength training and flexibility exercises.
3. Avoid Tobacco and Limit Alcohol
- Quit smoking to reduce the risk of coronary artery disease.
- Limit alcohol to recommended guidelines (one drink per day for women, two for men).
4. Manage Stress Effectively
- Practice mindfulness, meditation, or yoga.
- Prioritize work-life balance and seek support when needed.
5. Regular Health Check-Ups
- Monitor blood pressure, cholesterol, and blood sugar levels.
- Consult your doctor for screenings based on your age and risk factors.
Chronic Stress: How It Damages Your Health and Powerful Ways to Fight Back

Living with Heart Disease
If you are diagnosed with heart disease, managing the condition involves:
- Medication:
- Over the course of time, as the medications that are recommended for the management and prevention of symptoms were administered.
- Over the course of time, as the medications that are recommended for the management and prevention of symptoms were administered.
- Lifestyle Modifications:
- Sustaining the behavioral modification in regards to diet, exercise and stress.
- Sustaining the behavioral modification in regards to diet, exercise and stress.
- Support Systems:
- Logging into support groups or even seeking counseling as a result of the emotional stress that is likely to result from the illness.
- Logging into support groups or even seeking counseling as a result of the emotional stress that is likely to result from the illness.
- Regular Follow-Ups:
- Scheduling follow up appointments to the health care provider’s office to reassess progress and make changes.
- Scheduling follow up appointments to the health care provider’s office to reassess progress and make changes.
Final Thoughts
Cardiovascular illnesses continue to be a major factor in endangering the lives of people, but if the signs are detected early enough a lot can be done to improve the situation. It is therefore important that one starts practicing good health, especially heart health and take heart check ups often so that you may live a longer healthy life. It means staying up to date, learning how to be attentive to the signals the body sends and taking care of any possible heart issues. To get more articles related to this issue, check out other articles on Health Wander.
FAQ’S
Can heart disease symptoms differ between men and women?
Yes, men often experience classic symptoms like chest pain, while women may have subtler signs such as nausea, fatigue, and jaw or upper back pain.
What are silent heart disease symptoms?
Silent symptoms, such as mild discomfort, indigestion, or fatigue, may occur without noticeable chest pain, making them harder to recognize.
When should I see a doctor for heart-related symptoms?
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience persistent chest pain, severe shortness of breath, fainting, or radiating pain to the arms or jaw.
How is heart disease diagnosed?
Doctors use a combination of medical history, physical exams, and tests like ECG, echocardiograms, stress tests, and blood tests to diagnose heart disease.
Can lifestyle changes help prevent heart disease?
Yes, maintaining a healthy diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco, limiting alcohol, and managing stress can significantly lower your risk.
Is heart disease reversible?
While some damage may be irreversible, lifestyle changes and medical treatment can prevent progression and improve overall heart health.



